Actini
89
Ac
Grup
n/a
Període
7
Bloc
f
Protons
Electrons
Neutrons
89
89
138
Propietats Generals
Nombre atòmic
89
Massa atòmica
[227]
Nombre de massa
227
Categoria
Actínids
Color
Plata
Radioactiu
Sí
From the Greek aktis, aktinos, meaning beam or ray
Estructura cristal·lina
Cara cúbica centrada
Història
André-Louis Debierne, a French chemist, discovered actinium in 1899.
He separated it from pitchblende residues left by Marie and Pierre Curie after they had extracted radium.
Friedrich Oskar Giesel independently discovered actinium in 1902 as a substance being similar to lanthanum.
He separated it from pitchblende residues left by Marie and Pierre Curie after they had extracted radium.
Friedrich Oskar Giesel independently discovered actinium in 1902 as a substance being similar to lanthanum.
Electrons per capa
2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2
Configuració electrònica
[Rn] 6d1 7s2
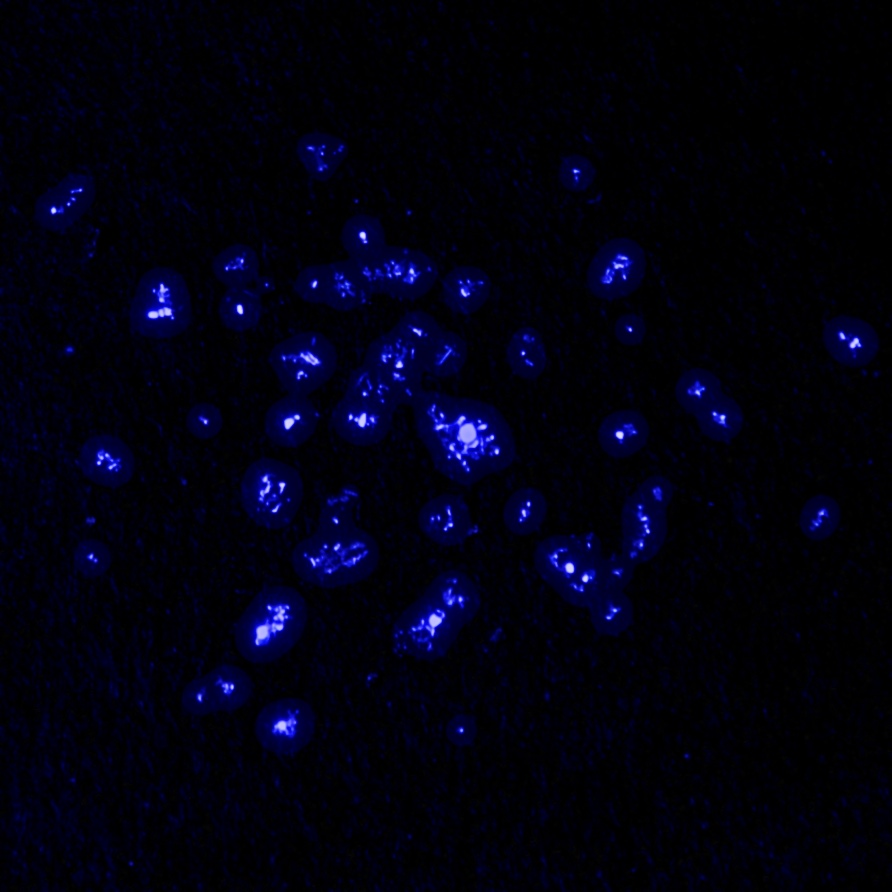
Actinium glows in the dark with a pale blue light
Propietats Físiques
Fase
Sòlid
Densitat
10,07 g/cm3
Punt de fusió
1323,15 K | 1050 °C | 1922 °F
Punt d'ebullició
3471,15 K | 3198 °C | 5788,4 °F
Entalpia de fusió
14 kJ/mol
Entalpia de vaporització
400 kJ/mol
Capacitat tèrmica específica
0,12 J/g·K
Abundància a l'escorça terrestre
n/a
Abundància a l'univers
n/a
Número CAS
7440-34-8
Número CID de PubChem
n/a
Propietats Atòmiques
Radi atòmic
-
Radi covalent
215 pm
Electronegativitat
1,1 (Escala de Pauling)
Potencial d'ionització
5,17 eV
Volum atòmic
22,54 cm3/mol
Conductivitat tèrmica
0,12 W/cm·K
Estats d'oxidació
3
Aplicacions
Actinium is used as an active element of radioisotope thermoelectric generators, for example in spacecraft.
The medium half-life of 227Ac makes it very convenient radioactive isotope in modeling the slow vertical mixing of oceanic waters.
225Ac is applied in medicine to produce 213Bi in a reusable generator or can be used alone as an agent for radiation therapy.
The medium half-life of 227Ac makes it very convenient radioactive isotope in modeling the slow vertical mixing of oceanic waters.
225Ac is applied in medicine to produce 213Bi in a reusable generator or can be used alone as an agent for radiation therapy.
Actinium is highly radioactive
Isòtops
Isòtops estables
-Isòtops inestables
206Ac, 207Ac, 208Ac, 209Ac, 210Ac, 211Ac, 212Ac, 213Ac, 214Ac, 215Ac, 216Ac, 217Ac, 218Ac, 219Ac, 220Ac, 221Ac, 222Ac, 223Ac, 224Ac, 225Ac, 226Ac, 227Ac, 228Ac, 229Ac, 230Ac, 231Ac, 232Ac, 233Ac, 234Ac, 235Ac, 236Ac